If you are in the quest for better health, understanding the role of various nutrients is crucial! One such essential nutrient is vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin. This water-soluble vitamin plays a significant role in numerous bodily functions, including the production of red blood cells and DNA synthesis. However, one of its lesser-known but equally essential roles is its impact on the immune system. Let’s explore the connection between vitamin B12 and the immune system, highlighting why maintaining adequate levels of this vitamin is vital for overall health.
The Role of Vitamin B12 in the Body
Before diving into its effects on the immune system, it’s essential to understand the general functions of vitamin B12 in the body. Vitamin B12 is crucial for:
Red Blood Cell Production
It helps form red blood cells, essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body.
DNA Synthesis
Vitamin B12 is necessary for adequately synthesizing DNA, the genetic material in all cells.
Nerve Function
It aids in maintaining the myelin sheath, which protects nerve fibers and ensures effective nerve signal transmission.
Energy Production
Vitamin B12 is involved in the metabolism of every cell in the body and plays a key role in energy production.
Given these critical functions, a vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to serious health issues, particularly concerning the impact on the immune system.
Vitamin B12 and the Immune System
The immune system is the body’s defense mechanism against infections, diseases, and foreign invaders. It contains various components, including white blood cells, antibodies, and other molecules that work together to protect the body. Vitamin B12 contributes to immune health in several ways:
White Blood Cell Production
Vitamin B12 is essential for the production and function of white blood cells, which are crucial immune system components. These cells detect and destroy pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances.
DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
The rapid production and division of immune cells are vital for a quick and effective immune response. Since vitamin B12 is crucial for DNA synthesis, it directly supports the rapid cell division required for a robust immune response.
Nervous System Support
The nervous system and immune system are interconnected. Vitamin B12’s role in maintaining a healthy nervous system indirectly supports the immune system, ensuring nerve signals regulating immune responses function correctly.
Reduction of Homocysteine Levels
Elevated homocysteine levels, often due to vitamin B12 deficiency, can lead to inflammation and a weakened immune response. Adequate vitamin B12 helps maintain low homocysteine levels, thus supporting immune function.
Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can significantly impact overall health, including immune function. Some common signs of deficiency include:
Fatigue and Weakness: Due to reduced red blood cell production and impaired oxygen transport.
Nerve Problems: Such as numbness, tingling, and difficulty walking, resulting from nerve damage.
Cognitive Issues: Including memory loss, confusion, and mood changes.
Pale or Jaundiced Skin: Due to impaired red blood cell production.
Shortness of Breath and Dizziness: Resulting from anemia.
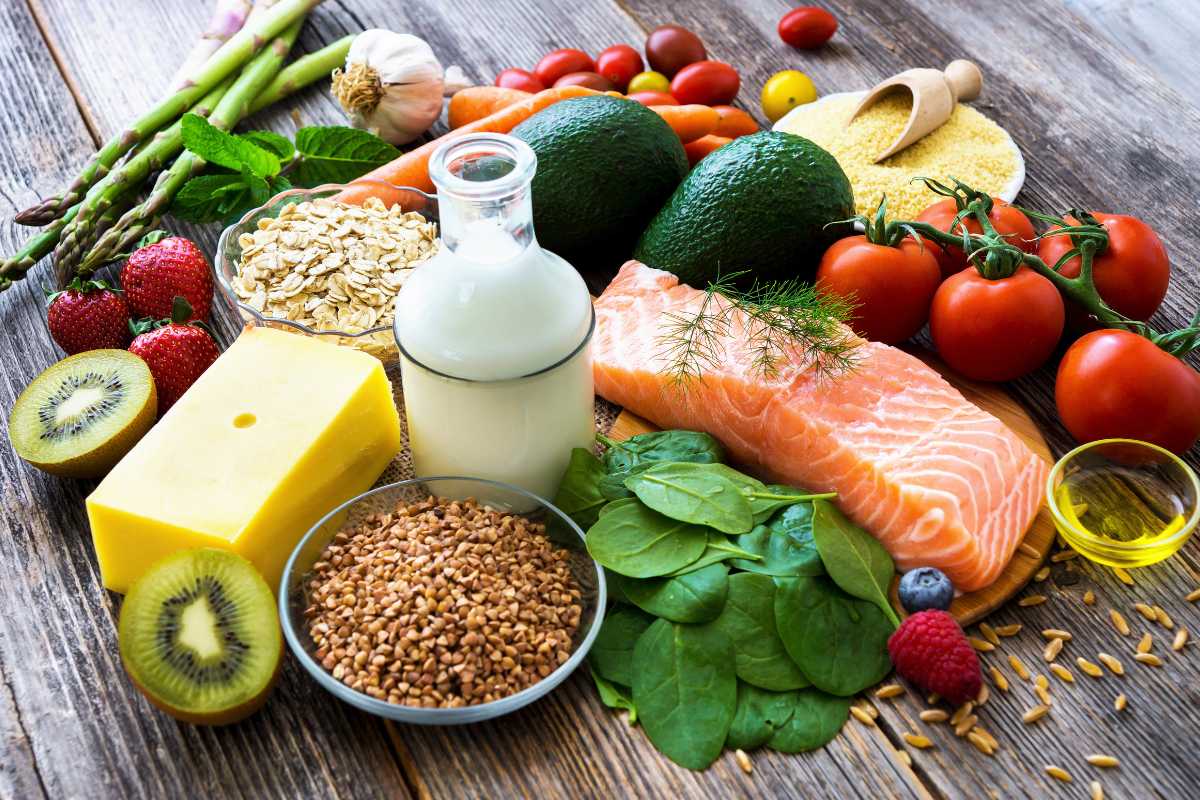
Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is naturally found in animal-based foods, making it essential for individuals who follow vegetarian or vegan diets to find alternative sources or supplements. Key dietary sources include:
Meat: Beef, pork, and lamb.
Fish: Salmon, trout, and tuna.
Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt.
Eggs: Particularly the yolks.
Fortified Foods: Such as fortified cereals and plant-based milk alternatives.
Supplementation and Dosage
For individuals at risk of deficiency, such as vegetarians, vegans, and older adults, supplementation might be necessary. Vitamin B12 supplements are available in various forms, including tablets, sublingual (under-the-tongue) preparations, and injections. The recommended daily intake varies by age, lifestyle, and specific health needs, so it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is indispensable for maintaining a healthy immune system. It plays a critical role in protecting the body against infections and diseases by supporting white blood cell production, DNA synthesis, and nerve function. Ensuring adequate intake of vitamin B12 through diet or supplementation can help maintain robust immune health and overall well-being. Learn more about vitamin b12 injections from our team at Advanced Medical Spas, a division of Advanced Urgent Care & Aesthetics.